News & Updates
Development of Core Technology for Skyrmion based Ultra-Low Power Devices to Advance the Age of A.I.
- Writerkrissadmin
- Date2021-11-05 00:00
- Hits20973
Development of Core Technology for Skyrmion
based Ultra-Low Power Devices to Advance the Age of Artificial Intelligence
-World's first implementation of skyrmion generation, deletion, and shift technology within a single device -
- Potential applications in the development of next generation ultra high density and ultra high speed memory devices-
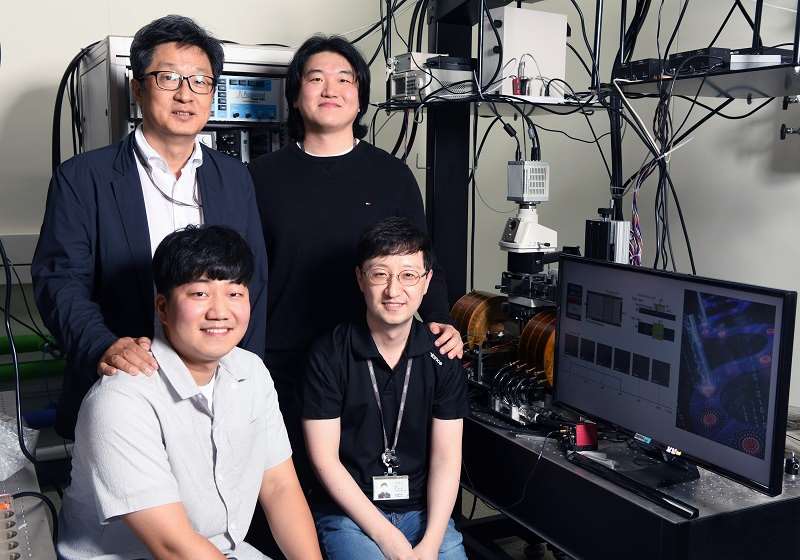

▲ The Quantum Spin Team of the KRISS Quantum Technology Institute
(Clockwise starting from the top left: principal research scientist Chanyong Hwang, senior research scientist Seungmo Yang,
principal research scientist Kyoung-Woong Moon, research student Tae-Seong Ju)
The Quantum Spin Team of the Quantum Technology Institute at the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science(KRISS, President Hyun-Min Park) successfully developed the core technology for the implementation of Skyrmion based electronic devices. This advancement is expected to contribute significantly in the development of neuromorphic and logic devices, which are next generation semiconductor devices.
Artificial intelligence and supercomputers consume massive amounts of power, so much that they are referred to as electricity guzzlers. The power consumption during a single round of Go by AlphaGo in 2016 was approximately 1MW, which is similar to the power consumption of 100 average households in a single day. As a result, there is increasing interest in ultra low power electronic devices that process large-capacity data with low power consumption.
A skyrmion is a spin structure in a spiral configuration. It can be reduced down to a few nanometers and its potential for ultra low power devices is highly anticipated as skyrmions can be transported with very little power. Electronic devices using skyrmions are economical as they consume 1/100 of the power of electronic devices that recorded 1s and 0s using the N and S magnetic poles.
To develop skyrmions into electronic devices, the technologies to implement the 4 operations of generation, deletion, shift, and detection to control individual skyrmions within a single device are necessary. Over the past decade, researchers have been successful in implementing combinations of these 4 technologies experimentally, however, experimentally demonstrating the implementation of all four operations in a single device has not been possible as the exact mechanism behind generation is yet undefined.
Up to now, research on electronic devices using skyrmions have been mostly based on computer simulations. For the commercialization of skyrmion based electronic devices, empirical verification is necessary, so there are limitations in developing devices with high application potential.
The Quantum Spin Team of the KRISS Quantum Technology Institute went beyond the method of skyrmion generation and deletion using strong external stimuli like light, electric current, magnetic field, and electric field limited to the 2-dimensional plane and was successful in experimentally implementing a novel skyrmion generation and deletion method based on a 3-dimensional vertical electrode structure.
The KRISS research team carried out current injection at a specific point of the magnetic layer using the formation of filaments that act as 3-dimensional vertical electrodes within the oxide layer. Generation and deletion of skyrmions were observed. This method was then integrated with the existing skyrmion shift technology to realize the technology for generation, deletion, and shift of skyrmions freely in a single device.
This technology can be easily applied to MRAM* technology under development in domestic companies and carries great significance in that the skyrmion racetrack memory, theoretically proposed by 2007 Nobel Prize for Physics Laureate, Dr. Albert Fert, was successfully implemented experimentally for the first time in the world.
* MRAM(Magnetic RAM): Referred to as a magnetic semiconductor, data is processed and stored utilizing the phenomenon of pushing and pulling the magnetic field. Theoretically, semiconductors with packing densities 1000 times that of DRAM can be manufactured.
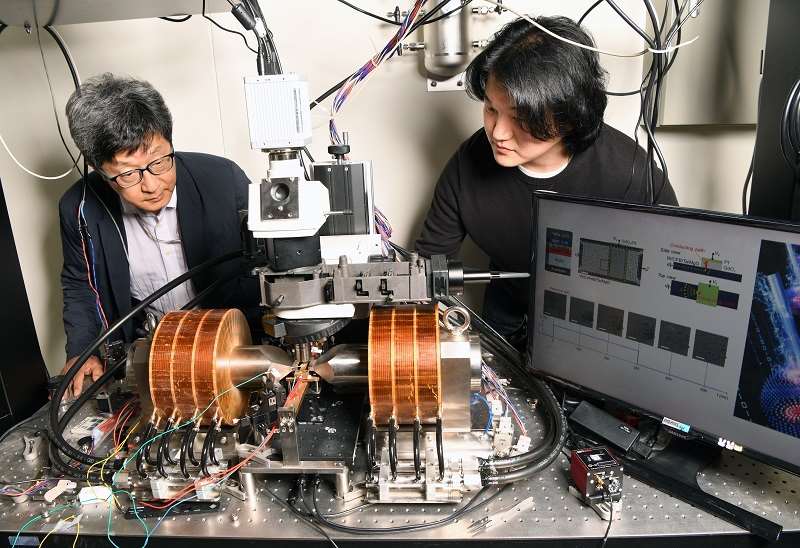
▲ KRISS Quantum Technology Institute Principal Research Scientist Chanyong Hwang(left)
and Senior Research Scientist Seungmo Yang(right) carry out experimentation using skyrmions.
KRISS Quantum Technology Institute Principal Research Scientist Chanyong Hwang said that “this accomplishment will play a key role in the development of next generation semiconductor technology” and that “in the near future, there are plans to carry out applied research regarding synaptic devices applying skyrmion number control and research on quantum skyrmions that was virtually impossible to conduct experiments.”
Funded by the Creative Materials Discovery Program and the Next Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Quantum Spin Team of the KRISS Quantum Technology Institute and the research team of DGIST Emerging Materials Science Department Professor Jung-Il Hong jointly participated in this research achievement, which was published online on September 27 in the world renowned academic journal Advanced Materials(IF: 30.849).
|
Terminology |
○ Skyrmion
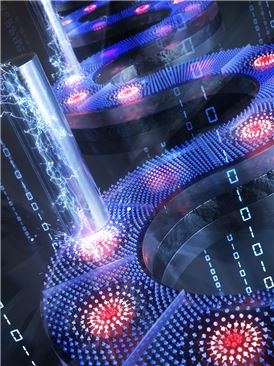
▲ Image representing a skyrmion device implementation using 3-dimensional vertical electrodes (Research accomplishment poster, selected as inside cover for the Advanced Materials paper) A skyrmion is a distinctive particle-like spin structure with the spindle arranged in a spiral configuration. Under the change in the external environment, skyrmions have a tendency to maintain its shape and structure, enabling their reduction in size down to a few nanometers and the number of skyrmions can be controlled electrically. These characteristics make skyrmions useful for applications in next generation electronic devices such as memory, logic devices, and communication devices. To apply skyrmions to memory devices, generation and deletion of individual skyrmions at desired positions have to be possible as well as transporting generated skyrmions at very high efficiency as each skyrmion is the base unit(bit) of information storage.
- Source: ○ Neuromorphic Neuromorphic refers to hardware like semiconductor chips made to mimic the human brain. The transfer of signals between the neurons of the brain is mimicked for efficient data processing. Power consumption is only 20W, so artificial intelligence(AI) can be implemented at ultra low power. |
QUICK MENU 원하시는 서비스를 클릭하세요!
등록된 퀵메뉴가 없습니다.