
News & Updates
Development of Quantum Direct Communication Technology Opens Door to Secure Quantum Networks
- Writerkrissadmin
- Date2021-03-03 00:00
- Hits11217
Development of Quantum Direct Communication Technology
Opens Door to Secure Quantum Networks
-Direct transmission of data without risk of eavesdropping, gaining attention as foundation
for next-generation quantum communication technology -
- Outcome of joint research between KRISS and NSR,
operation of test quantum communication network across the two institutions -
The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS, President Hyun-Min Park) and National Security Research Institute (NSR) have succeeded in the joint development and test operation of quantum direct communication technology.
The quantum direct communication technology proposed by KRISS and NSR is the first of its kind in the world. The two institutions worked together closely from the planning stage of the project, sharing information on core technology and obtaining publications and intellectual property rights related to quantum direct communication.
Quantum communication transmits data carried by photons, the smallest unit of light, to eliminate the possibility of eavesdropping. Quantum direct communication in particular allows secret messages to be directly transmitted through quantum channels, without separating the message and the key.
Existing quantum communication technology uses very weak photon-level laser pulses to share random keys between the transmitter and receiver.
For example, quantum key distribution, which recently reached the commercialization phase, requires the two users to share a secret key and transmit messages separately, which results in the challenge of managing the large number of secret keys generated when the number of users increases.
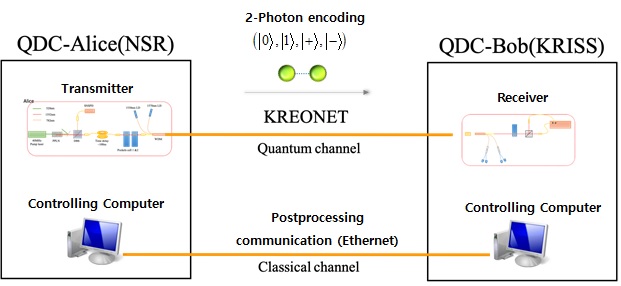
▲ Schematic diagram of quantum direct communication
However, in quantum direct communication, secret messages are sent directly between users, without the issue of secret key management following an increased number of users. To achieve this, new technologies for single-photon source, detector, channel control, and protocol design and testing are required, alongside technologies to compensate for low light detection efficiency, optical loss or distortion in real world environments.
Researchers from KRISS and NSR developed the relevant technologies and successfully achieved quantum direct communication in the state-use quantum cryptography test network (KRISS-KISTI-NSR, approx. 20 km, provided by Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information(KISTI)).
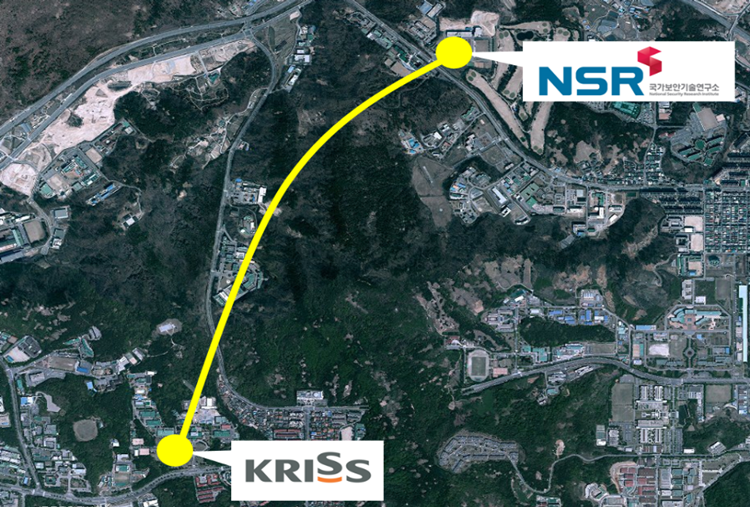
▲ Connection between KRISS and NSR
KRISS researchers were in charge of developing the single-photon source and measurement equipment, while NSR researchers were in charge of system construction and network building for quantum direct communication. The transmitter was installed on the KRISS premises, while the receiver was placed in NSR.

▲Quantum direct communication testing area
In the test operation, several hundred Hz of secure data was transmitted, while quantum bit error rate (QBER), a measure of communication security, was at a similar rate to existing quantum key distribution technology at 3% to 6%.
The two institutions also conducted joint research on quantum simulators. Through this, they developed quantum information processing technology using atoms, superconducting single photon detector technology, and technology for interconnecting quantum-communication and internet links in actual communication networks.
Director of the KRISS Quantum Technology Institute Hee Su Park commended the effort, remarking, “we have been able to achieve advanced quantum communication using independently developed technology for the first time, thanks to smooth convergence in research between the two organizations,” adding, “this achievement will not only serve as elementary technology for quantum communication, but also become a foundation for quantum computing technology.”
The elementary technologies developed for this project were published in the international journals such as Optics Express (IF: 3.669) and Metrologia (IF: 3.447), and 6 domestic and international patents were registered in relation to the project.
QUICK MENU 원하시는 서비스를 클릭하세요!
등록된 퀵메뉴가 없습니다.
