KRISS Develops Microwave Frequency Comb Generation Technology
- Writerkrissadmin
- Date2022-08-11 00:00
- Hits552
KRISS Develops Microwave Frequency Comb Generation Technology Using Superconducting Nanoelectromechanical Device
- Expected to benefit high-performance nanosensors making precise mass measurements -
Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS, President Hyun-Min Park) has developed a technique of generating microwave frequency combs using a superconducting nanoelectromechanical transducer developed in 2021. The frequency combs can be utilized in high-performance sensors that require precise molecular-level mass measurements.

▲ Principal researcher Junho Suh (left) and senior researcher Jinwoong Cha (right) of the KRISS Hybrid Quantum Systems Team
The KRISS Hybrid Quantum Systems Team developed a technique to produce frequency combs by introducing microwave signals into a superconducting nanoelectromechanical device*. A frequency comb is a phenomenon where multiple frequency signals are equally spaced, exhibiting a comb-like appearance. The frequency combs generated by the research team equals to the resonant frequency of the nanomechanical device, and measuring the comb-frequency spacing could allow for precise tracking of frequency changes.
* Superconducting nanoelectromechanical device: A nanoscale device, made of a superconducting material, that allows electrical measurements of mechanical vibration
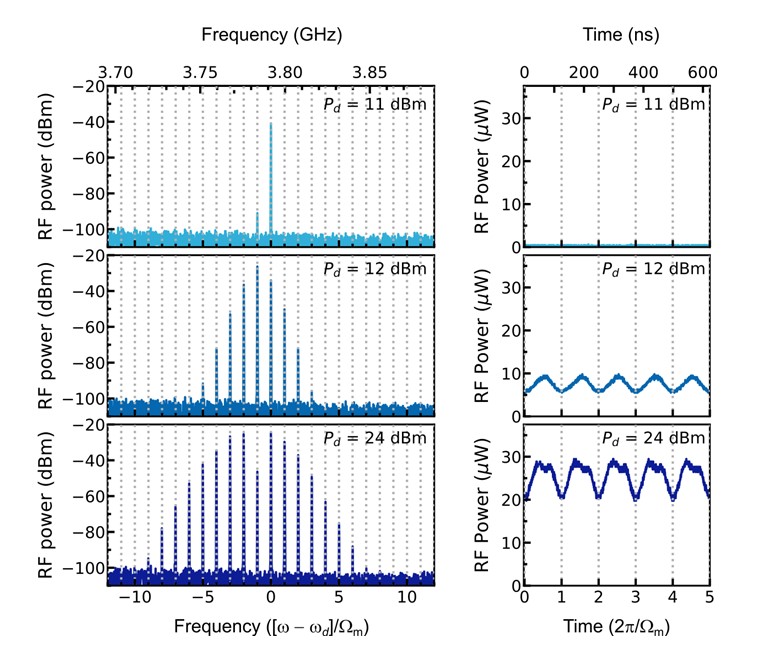
▲ Microwave frequency combs obtained from the superconducting nanoelectromechanical device
The team placed the device in a liquid-helium freezer to provide a low-temperature environment needed for superconducting performance. A microwave signal generator was used to transmit a single frequency microwave signal to the device, and frequency combs were successfully formed.
The typical method to measure the frequency of a nanomechanical device is based on optical interference caused by light waves reflected from the device. The frequency of the interference signals from the nanomechanical device must be compared against electrical signals of a certain frequency for real-time tracking. However, this approach requires complex optical and electrical equipment, resulting in poorer measurement performance due to the various noise sources.
▲ Schematic showing the generation of microwave frequency combs in a superconducting nanoelectromechanical device
The principle behind the frequency comb generation is that the resonant frequency of the nanomechanical device can be measured by introducing single-frequency microwave signals, even without the use of complex sets of equipment.
The technique has vast applications in areas requiring precise measurements such as high-performance nanosensors. For instance, the resonant frequency of a nanomechanical device changes when protein molecules are adsorbed because of the change in the mass of the device. It is possible to estimate the mass of the adsorbed material by analyzing frequency comb signals.
Jinwoong Cha, senior researcher of the Hybrid Quantum Systems Team, said, “The frequency comb generation technique will lead to enhancement of the precision by at least a few dozen times that of existing nanomechanical sensors.”
Junho Suh, the principal researcher who also participated in the project, said, “Although this experiment was conducted at ultra-low temperatures to maximize device performance, we aim to realize frequency combs at the room temperature to utilize this technique in industrial applications.”
This study, funded by KRISS, National Research Council of Science and Technology, and National Research Foundation of Korea, was published in the world-leading journal Nano Letters (IF: 12.262) in June.

