New technology improves accuracy of radiation therapy nationwide
- Writerkrissadmin
- Date2020-08-13 00:00
- Hits666
New technology improves accuracy of radiation therapy nationwide
- Measurement standard technology to bridge gap in radiation quality across hospitals -
The Dosimetry Metrology Team of the Ionizing Radiation Metrology Group at Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS, President Hyun-Min Park) developed a measurement standard technique to enhance the accuracy of radiation therapy.
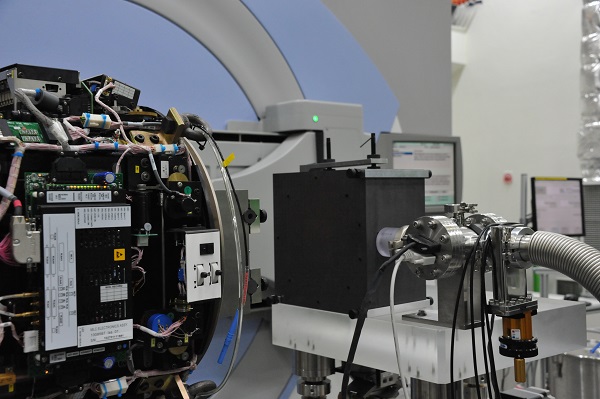
▲ The graphite calorimeter developed by the research team of KRISS (a black box on the right side)
The proposed technology is expected to enhance the accuracy of radiation treatment, and bridge gaps in radiation quality across hospitals. This technology has been developed and secured by only seven countries in the world, namely, the United States, United Kingdom, France, Canada, Germany, Japan, and Korea.
In radiation therapy, high energy X-rays are used to kill cancer cells. It is a commonly employed treatment for cancer, along with surgery and anticancer drugs. More than 30% of cancer patients in Korea are receiving radiation therapy.

▲ An inside image of the graphite calorimeter developed by the research team of KRISS
Medical professionals and advanced equipment are necessary for accurate, effective radiation therapy. Advanced equipment should be capable of delivering a precise amount of radiation to targeted areas.
The International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) recommends a dose delivery uncertainty of no more than 5%. That is, equipment must be regularly managed to meet accuracy requirements.
Differences exist across equipment no matter how expensive, and radiation properties are subject to change over time. Regular calibration is needed to maintain the dose delivery of radiation equipment.
The problem is that the reference radiation is different for calibration and equipment used in treatment. Radiation treatment equipment have shifted from using gamma rays of the radioactive isotope cobalt-60 to high energy X-rays from medical linear accelerators.
? High energy X-rays allow energy changes in consideration of patient’s build and target area, and dose delivery can be adjusted for more effective treatment.

▲ A result of the international comparison in water absorption dose for high energy X-rays from medical linear accelerators
While both types of radiation involve photons, they require calibration using theoretical formulas to compensate for their different energies. This has inevitably led to an increase in the uncertainty of radiation dose in hospitals. Moreover, there is a gap in radiation quality across hospitals due to the significant difference in equipment costs.
The team developed a technique that determines dose in an absolute manner regardless of radiation energy. The absolute measurement offers greater precision than relative comparison. The significance of the calorimetric technique lies in measuring the increase in medium temperature at a high precision of tens of μK.

▲ Principal researcher In Jung Kim of KRISS is measuring absorption dose using the graphite calorimeter developed by his research team
Using graphite as a medium, the team measured the increase in graphite temperature when it was exposed to radiation. Next, they multiplied specific heat. By applying the dose conversion factor from graphite to water obtained through Monte Carlo simulations, they determined the accurate dose for water, which is similar to the human body.
Principal researcher In Jung Kim said, “Calibration services are being provided for calorimeters, and hospitals can utilize them to halve the dose uncertainty. We will continue to actively participate in improving the quality of dose measurements in hospitals at home and abroad.”

▲ The Dosimetry Metrology Team of the Ionizing Radiation Metrology Group at KRISS
From left, Jung Kim(Principal researcher), Byoung-chul Kim(Senior researcher), Yunho Kim(Senior researcher), Chul-young Yi(Principal researcher)
Supported by the Radiation Research Infrastructure Expansion Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT, the study was published in the prestigious international journal Metrologia (IF: 3.447).

